The traditional income statement, also called absorption costing income statement, uses absorption costing to create the income statement. This income statement looks at costs by dividing costs into product and period costs. In order to complete this statement correctly, make sure you understand product and period costs. According to accounting tools, the primary item on an absorption income statement is gross revenues for the period.
Cost of Goods Sold and The Income Statement for Manufacturing Companies
- This means that we now need to remove the effect of over-absorbing $40000, which can be done simply by subtracting it from the cost of sales.
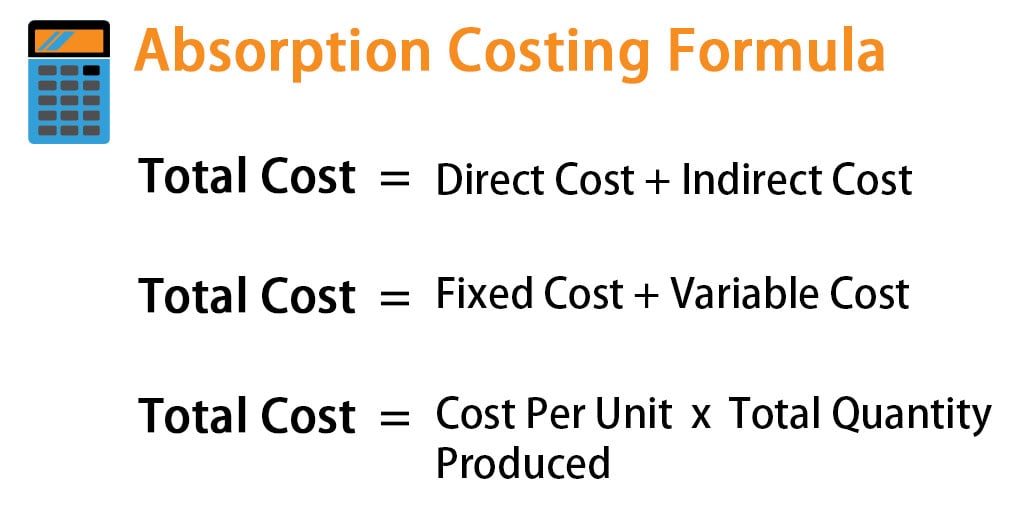
- Under absorption costing, all manufacturing costs, both direct and indirect, are included in the cost of a product.
- In summary, absorption costing principles provide businesses with an accurate, GAAP-compliant accounting method to incrementally track product profitability changes tied to production volumes.
- This is because an absorption cost includes manufacturing products, employees’ wages, raw materials, and every other production cost.
External reports are generated for public consumption; in the case of publicly traded corporations, shareholders interact with external reports. External reports are designed to reveal financial health and attract capital. It is very important to understand the concept of the AC formula because it helps a company determine the contribution margin of a product, which eventually helps in the break-even analysis. The break-even analysis can decide the number of units required to be produced by the company to be able to book a profit.
Revenue Reporting in Absorption Costing
Consequently, income before income taxes under variablecosting is $600 less than under absorption costing because morecosts are expensed during the period. If absorption costing is the method acceptable for financial reporting under GAAP, why would management prefer variable costing? Advocates of variable costing argue that the definition of fixed costs holds, and fixed manufacturing overhead costs will be incurred regardless of whether anything is actually produced. Absorption costing can skew a company’s profit level due to the fact that all fixed costs are not subtracted from revenue unless the products are sold.
Please Sign in to set this content as a favorite.
The method includes direct costs and indirect costs and is helpful in determining the cost to produce one unit of goods. The absorption costing method adheres to GAAP and provides an accurate, full-cost valuation of inventory. While more complex than variable costing, absorption costing gives managers and investors a clearer view of product profitability. Absorption costing leads to more accurate product costs than variable costing, which only includes direct costs. However, absorption costing depends heavily on cost estimates and output assumptions. In summary, absorption costing provides a comprehensive look at per unit costs by incorporating all expenses related to production.
What’s the Difference Between Variable Costing and Absorption Costing?
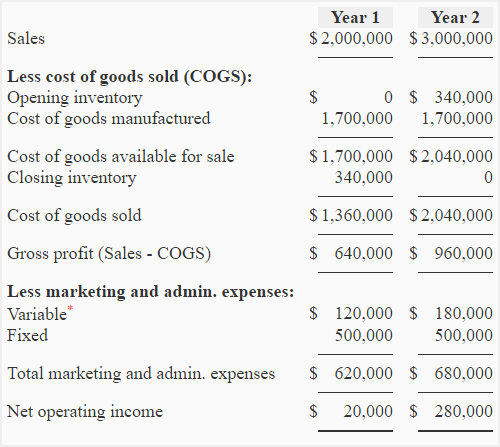
The basic format is to simply show the sales less the cost of goods sold equal gross profit. And also show the gross profit less the selling and administrative expenses and that equals the operating income. Absorption costing is not as well understood as variable costing because of its financial statement limitations. But understanding how it can help management make decisions is very important. See the Strategic CFO forum on Absorption Cost Accounting that helps managers understand its uses to learn more. To complete periodic assignments of absorption costs to produced goods, a company must assign manufacturing costs and calculate their usage.
Impact Of Inventory
By allocating fixed costs to inventory, absorption costing provides a fuller assessment of profitability. This causes net income to fluctuate between periods under absorption costing. Companies using absorption costing must understand these inventory valuation implications for accurate financial statement analysis when production volumes change. If you remember marginal costing, you will remember that we used the sum of marginal variable costs. Absorption costing, also known as marginal costing, variable costing, direct costing, or full costing, assigns all the costs of manufactured products.
Here, we are going to discuss the income statement under absorption costing and see how the net profit differs. Before we look at the income statement, is this tax deductible medical expenses let us have a look at what absorption costing is. The cost of goods sold (COGS) is calculated when the ending inventory dollar value is subtracted.
To arrive at the cost of closing inventory, we simply have to multiply the number of units with the absorption cost i-e $8 to arrive at $240,000. Overall, this statement is much easier to make if you understand product and period costs. Calculate the unit cost first, as that is the most difficult portion of the statement.
Carrying over inventories and overhead costs is reflected in the ending inventory balances at the end of the production period, which become the beginning inventory balances at the start of the next period. It is anticipated that the units that were carried over will be sold in the next period. If the units are not sold, the costs will continue to be included in the costs of producing the units until they are sold. This treatment is based on the expense recognition principle, which is one of the cornerstones of accrual accounting and is why the absorption method follows GAAP.

